How to Build Real-Time Interoperability Between EMR and Lab Systems
Timely and precise lab data is critical for diagnosis, treatment, and patient safety in the hectic clinical setting. However, many healthcare providers continue to use old, batch-based interfaces between their electronic medical records and laboratory systems, resulting in delayed results, manual entry mistakes, and service fragmentation.
To completely speed up operations and improve patient outcomes, businesses must adopt real-time integration between EMR and lab systems. This entails allowing systems to communicate and process information as soon as it becomes available without human intervention or lag.
In this blog, you’ll know the step-by-step approach to achieving real-time interoperability and learn key best practices for a smooth integration journey.
Why Real-Time Interoperability Matters
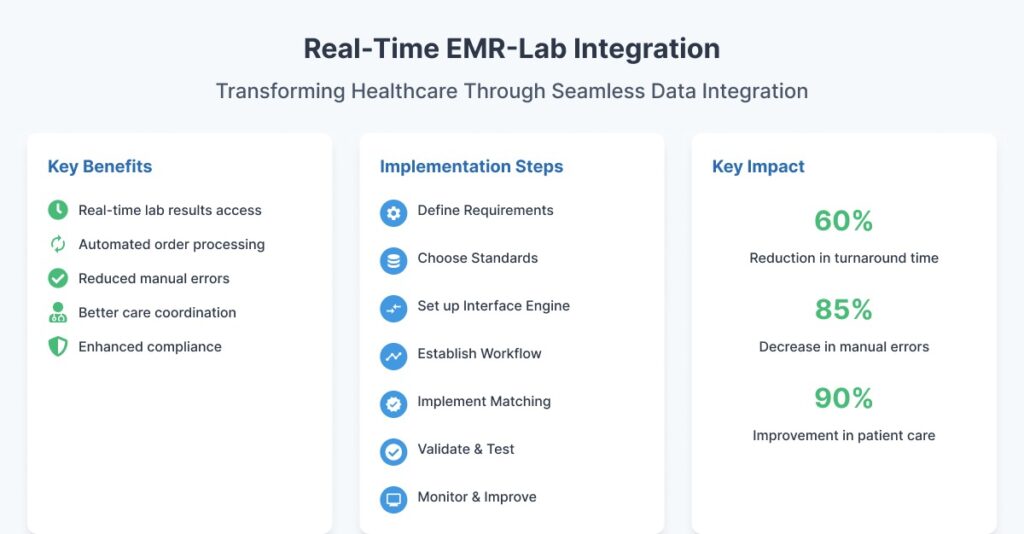
Compared to standard, irregular data transfers, real-time integration of EMRs and lab systems offers significant benefits. It decreases pointless testing, increases patient involvement, and empowers clinicians to make clinical decisions more quickly.
- The EMR provides instant access to lab findings.
- Automated order confirmations and status updates
- Reduced manual data entry and transcribing mistakes.
- Improved care coordination among departments.
- Increased regulatory compliance and data traceability.
Real-time interoperability allows for a closed-loop diagnostic workflow from test ordering to results reporting to clinical action, all in minutes.
Step-by-Step to Build Real-Time Interoperability
1. Define the Clinical and Technical Requirements
The first step in achieving real-time interoperability is to explicitly identify both clinical and technological objectives. This guarantees that the integration supports your operations, not merely system connectivity.
- Key topics to address: What lab tests are commonly ordered?
- Which EMR modules will need lab data integration, such as orders, outcomes, and dashboards?
- Is there a goal turnaround time for certain tests, like statistical orders?
- What standards does your lab system and EMR support, such as HL7 v2 and FHIR?
- Who will manage interface maintenance, support, and upgrades?
Engage clinical, IT, and lab operations stakeholders early in the process to ensure alignment on priorities and expectations.
2. Choose the Right Integration Standards
Standards are critical to ensuring interoperability between disparate systems. For real-time EMR-lab connection, HL7 v2 is the most extensively used communications system; however, FHIR is gaining popularity for contemporary, API-based exchanges.
Common HL7 message types are:
- ORM: Outbound lab orders from EMR to LIS
- ORU: Lab results from LIS to EMR.
- ACK – Acknowledgment messages confirm message receipt.
FHIR use cases can include:
- RESTful APIs for retrieving lab results.
- SMART-on-FHIR apps for visualizing diagnostic trends.
- Integration of mobile or third-party platforms.
Choose a protocol depending on system compatibility, scalability, and required data granularity.
3. Set up Bi-Directional Interface Engine
To allow real-time, two-way communication, you’ll need an interface engine to route, convert, and validate communications between the EMR and the LIS.
A real-time interface engine’s key capabilities include:
- Message translation, such as from HL7 to FHIR or vice versa.
- Field mapping and normalizing, such as test codes and units.
- Real-time routing and failover logic
- Monitor and alert for message failures
- Data throttling, queue management
Mirth Connect, Rhapsody, and Corepoint are popular engines that provide HL7/FHIR translation, scripting, and real-time throughput.
4. Establish a Lab Order and Result Workflow
To guarantee easy interoperability, create a closed-loop lab workflow that incorporates all stages of the lab communication process.
The real-time workflow should include:
- Order Placement – Clinician enters lab order in EMR. ORM message is sent to LIS.
- Order Acknowledgement – LIS confirms receipt with an ACK.
- Sample Collection and Processing – The LIS updates order status in real time.
- Result Reporting – LIS sends results via ORU, and EMR receives and assigns them to patient records.
- Clinician Review and Action – The provider receives an alert, evaluates the results, and takes clinical action.
Ensure that each system is configured to log and display statuses to the end user, as well as enable notifications for abnormal results.
5. Implement Patient and Test Code Matching
Real-time integration is only effective if both systems accurately identify and match patient IDs and test codes. Mismatches here can result in lost results, incorrect patient information, or integration failures.
Best Practices:
- Use a Master Patient Index to synchronize patient identifiers.
- Standardize lab test codes via LOINC.
- Use reconciliation tools to identify inconsistencies in names, DOBs, or test settings.
- Conduct regular audits of mappings between local and standardized terminologies.
Before going live, the lab and EMR teams should test together to ensure that the test catalogs are aligned.
6. Validate and Test the Integration
Before deploying real-time lab integration in a live clinical setting, perform extensive unit, integration, and user acceptance testing.
Testing must contain:
- Multiple test scenarios like routine, statistics, and canceled orders.
- Edge instances include incomplete returns, missing fields, and delayed replies.
- Load testing simulates peak lab volumes.
- User validation by clinicians and lab technicians.
Document all activities, intended results, and backup plans in the event of integration problems.
7. Monitor Performance and Continuously Improve
Once operational, real-time interfaces must be constantly monitored to ensure reliability and efficiency. A broken or delayed interface has a direct impact on patient care and lab operations.
Key monitoring metrics include interface uptime and transaction volume.
- Message transmission time.
- Error logs and failed messages.
- Order results turnaround times.
- Duplicate orders or mismatched outcomes.
Create dashboards and real-time notifications to monitor these metrics. In order to resolve problems and schedule updates, review them frequently during joint EMR-lab governance meetings.
Related: How to Overcome the Challenges of Lab Integration in OpenEMR
Streamline Lab-EMR Connectivity with CapMinds
Struggling with slow lab result turnarounds or manual data entry between your EMR and lab systems?
CapMinds delivers real-time interoperability solutions that eliminate delays, reduce errors, and enhance clinical workflows so your team can focus on what matters most: patient care.
Whether you’re integrating a new LIS or upgrading your current lab interface, our expert team ensures secure, standards-based connectivity from start to finish.
Our Real-Time Lab Integration Services Include:
- HL7 & FHIR-based bi-directional data exchange
- Interface engine setup and configuration (Mirth, Rhapsody, Corepoint)
- Lab order/result mapping with LOINC standardization
- Patient identity matching and MPI integration
- Real-time monitoring dashboards and ongoing support
Let CapMinds power your lab interoperability journey.
Get in touch with us today to build a faster, smarter, and more connected lab-to-EMR ecosystem.