HIE Integration Done Right: Avoiding Latency, Duplicates, and Identity Errors
Data sharing among hospitals, clinics, laboratories, and public health organizations is crucial for enhancing patient care and minimizing systemic inefficiencies. HIEs enable this by allowing the safe movement of patient health records across several platforms. However, successful HIE integration requires more than simply a link; it must also ensure data quality, speed, and patient safety.
Healthcare organizations that fail to handle latency, duplication, and identify problems frequently face issues in service delivery, diagnostic confusion, and even regulatory noncompliance.
In this blog, you’ll learn to know how to approach HIE integration correctly, with an emphasis on avoiding the most typical errors.
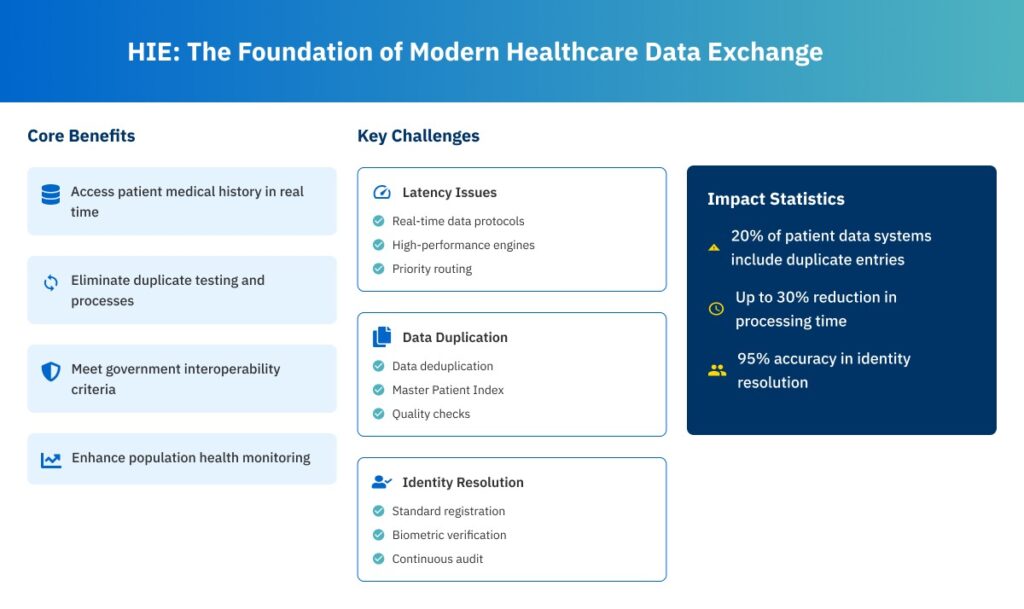
HIE -The Foundation of Modern Healthcare Data Exchange
Health Information Exchange acts as a middleman, allowing various EHRs and health IT systems to connect. Integrating with an HIE enables providers to:
- Access a patient’s medical history in real time.
- Eliminate duplicate testing and processes.
- Meet the government criteria for interoperability.
- Enhance population health monitoring and care coordination.
Despite these advantages, many businesses struggle with the deployment and optimization of their HIE connections. That’s because genuine interoperability entails more than just technological connectivity. It also necessitates data governance, identity resolution, and process alignment.
The Hidden Cost of Latency in HIE Transactions
Latency in HIE data sharing can dramatically impact patient care. Slow data access can lead to treatment gaps, provider irritation, and even patient discontent.
The following are some common reasons for latency:
- Inadequately optimized interface engines
- Lack of real-time data synchronization mechanisms
- Excessive system burden due to batch data processing
- Insufficient bandwidth or cloud resource allocation
To manage latency, healthcare organizations must:
- Implement real-time data protocols such as WebSockets and HL7 FHIR subscriptions.
- Set up high-performance integration engines with load balancing and fault-tolerant designs.
- Prioritize data routing rules to improve the flow of high-priority clinical information.
Fast, dependable data sharing is a must for time-sensitive healthcare environments including emergency rooms, critical care units, and telemedicine consultations.
Managing Duplicates: Clean Data or Clinical Risk?
Data duplication is a common issue in HIE integration. Duplicates reduce the quality of service, whether it’s a patient registered under many names or the same clinical remark repeated across multiple systems.
The ONC estimates that up to 20% of patient data systems include duplicate entries. These duplicates may result in:
- Contradictory medical histories
- Duplicate tests or procedures
- Incorrect medication reconciliation
- Increased administrative workload
To avoid duplicates during HIE integration, organizations should:
- Use data deduplication methods to standardize and match information such as name, DOB, and address.
- Create a Master Patient Index that assigns unique IDs across systems.
- Automate record reconciliation workflows and identify potential duplicates for human review.
Investing in advanced data matching technologies and continual quality checks allows providers to assure a single, unified patient record rather than a patchwork of partially correct ones.
Resolving Identity Errors at the Root
Differences in patient identities are a major risk to patient safety and are not just an administrative problem. Inaccurate diagnoses, unidentified allergies, and even unsuitable surgeries might arise from mistaken identities.
Identity problems in HIEs generally come from:
- Inconsistent demographic data between systems
- Errors in manual entry during patient intake
- Lack of universal patient IDs
- Poorly set MPI matching thresholds
To prevent identity mistakes, organizations should:
- Standardize patient registration processes for all involved businesses.
- Use probabilistic and deterministic matching methods to examine various demographic fields.
- Incorporate biometric verification or two-factor authentication, when applicable.
- Continuously audit MPI matches to detect false positives and missing matches.
Patient identity integrity is a critical component of good care. Without a trustworthy identification framework, HIEs cannot provide reliable or actionable information.
Aligning EHR Workflows with HIE Integration
Even the best integration cannot succeed without clinical workflow alignment. Data from an HIE should be smoothly integrated into the EHR interface and decision-making process.
Challenges include:
- Data occur in non-actionable areas of the EHR.
- HIE alerts or results are lost in email queues.
- Clinicians ignore HIE feeds because of previous irrelevant outcomes.
To address these workflow misalignments:
- Map incoming HIE data to therapeutically important areas in the EHR, such as patient summary views and progress notes.
- Integrate clinical decision support logic to highlight key data elements.
- Enable provider feedback loops to identify unnecessary or low-value data.
- Provide user training and documentation to encourage HIE feature uptake.
A seamless process encourages doctors to trust and use HIE data, making it an integral component of patient care rather than an afterthought.
Security, Compliance, and Patient Consent
HIE integration must satisfy legal requirements like HIPAA, TEFCA, and the 21st Century Cures Act in addition to performance and data quality. This entails turning on role-based access control, access logs, and end-to-end encryption.
Also, several states and HIEs use an opt-in or opt-out consent mechanism. Providers must respect a patient’s wishes for data sharing.
The best practices for compliance and trust are:
- Encrypt all PHI in transit and at rest.
- Use OAuth 2.0 and SMART on FHIR to secure API access.
- Use audit logs to keep track of all access to patient records.
- Integrate consent management modules into the EHR.
Security is more than simply IT; it is about establishing trust between patients, providers, and technology.
Monitoring and Maintenance for Post-Go-Live Success
Launching an HIE integration is only the start. Without continuous monitoring, even the greatest systems decline over time owing to:
- Version mismatches
- API updates from third-party systems
- Latency creep
- Data mapping errors following EHR upgrades
Related: Achieving Interoperability at Scale: HL7, FHIR, and API Integrations with OpenEMR
HIE Integration with CapMinds
Struggling with slow data exchange, duplicate records, or patient identity errors in your HIE integration?
CapMinds can help you overcome these roadblocks with precision-engineered healthcare interoperability solutions. Our experts specialize in building high-performance, secure, and fully customized HIE integrations tailored to your health system’s needs.
From seamless data exchange to reliable identity resolution, we ensure your clinical workflows stay efficient and error-free. With CapMinds, you get:
- HL7/FHIR-based integration with any HIE or EHR
- Master Patient Index (MPI) setup and optimization
- Real-time data syncing with latency-free performance
- HIPAA-compliant security and consent management
- Continuous monitoring and post-go-live support
Ready to transform your interoperability strategy? Partner with CapMinds to build faster, smarter, and cleaner HIE connections that drive better care. Contact us today to get started.