Modular EHR Architecture: The Smart Way to Extend Core EMRs Without Full Replacement
Legacy EMR systems are recognized for their inflexible data models, compartmentalized processes, and lengthy update periods of several years. However, most US hospitals cannot just remove a platform that affects every clinical, financial, and regulatory procedure.
Modular EHR design provides a realistic middle ground, allowing CIOs, CMIOs, and health-IT architects to add new features to an existing EMR while ensuring availability and data integrity.
In this blog, you’ll learn how modern EHR helps in extending core EMRs without fully replacing the architecture.
Monolithic EMRs Collide With Modern Care
Throughout the 2010s, hospitals deployed corporate EMRs to take advantage of Meaningful Use incentives. These systems achieved their function of centralizing paperwork and billing, but many today struggle to support:
- Telehealth volumes increased 38-fold during the pandemic, yet older EMRs seldom incorporate frictionless video visit scheduling, device capture, or telehealth payment systems.
- Lab data interchange, specialty-specific applications, and remote patient monitoring systems often require expensive, bespoke interfaces.
- Clinicians want mobile-first, intuitive interfaces, but monoliths provide desktop-centric displays that reduce productivity.
- CMS, ONC, and state laws change quarterly; waiting for vendor upgrade cycles causes compliance gaps.
Why Full Replacement Rarely Works
- The cost of replacing an enterprise EMR for a multi-facility health system can surpass $100 million, including hardware, license, training, and downtime.
- Forced go-lives produce steep learning curves, resulting in documentation backlogs and physician fatigue.
- Historical orders, imaging, and discrete vitals frequently demand unique mapping; mistakes endanger patient safety.
- Revenue-cycle disruptions and scheduling delays can reduce operational profits for months.
According to Gartner, 60% of healthcare core-system replacements run late or over budget. Modular EHR architecture avoids these minefields.
What Exactly is Modular EHR Architecture?
A modular design then surrounds that core with lightweight, purpose-built components, generally hosted in the cloud, and connects them via secure APIs and message brokers.
| Layer | Purpose | Typical Technologies |
| Interface Engine | Routes HL7, FHIR, XDS, and DICOM messages | Mirth Connect, Rhapsody, InterSystems Ensemble |
| API Gateway | Secures and throttles RESTful traffic | AWS API Gateway, Kong, Apigee |
| Microservices | Encapsulate discrete functions (e.g., e-prescribe) | Docker, Kubernetes, serverless |
| Smart Middleware | Transforms data, orchestrates workflows | Node.js, .NET Core, Spring Boot |
| UX Components | Web/mobile front ends, clinician portals | React Native, Flutter, Angular |
High-value Use Cases
1. Integrating Telehealth and EMRs
- Automatically generate telehealth appointments from existing scheduling tables.
- Embed WebRTC or third-party video links into the encounter screen.
- Sync encounter notes and CPT codes into the EMR for billing.
2. Lab Data Exchange
- Real-time HL7 ORU communications from external reference laboratories.
- FHIR subscriptions that automatically fill results and highlight crucial values.
3. Telehealth Billing Systems
- Capture patient-entered vitals, consent, and copayment via a pre-visit micro-app.
- Automatically verify place-of-service codes and telehealth modifiers (95, GT).
4. Virtual Care Workflow
- Chronic-care displays that collect weight and blood pressure data from linked devices.
- Patient-generated questionnaires emerged in clinicians’ inboxes.
5. Connected Care Platforms
- Push discharge summaries to skilled-nursing EHRs via Direct messaging.
- Obtain ADT feeds from community HIEs to close referral loops.
These modules foster a best-of-breed ecosystem, allowing specialist clinics to implement niche solutions while maintaining the enterprise EMR that serves as the foundation for enterprise reporting and compliance.
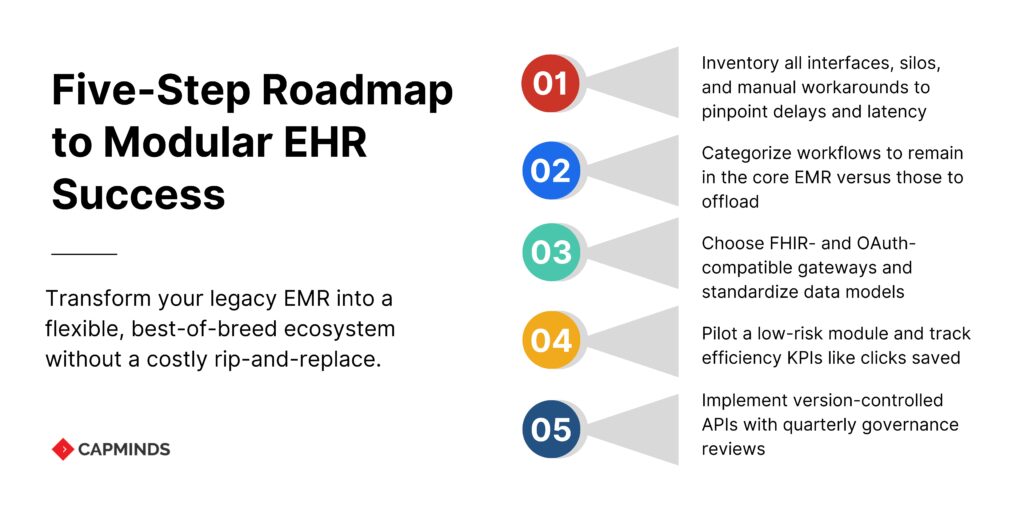
Five-Step Roadmap to Implementing a Modular Strategy
1. Map your Current State
- This includes inventory interfaces, data silos, and manual workarounds.
- Catalog issues include telemedicine scheduling delays, test result latency, and reimbursement rejections.
2. Define an “Innovation Perimeter”
Determine which workflows will stay in the EMR (meds administration, ADT) and which may be outsourced (patient interaction, specialized documentation).
3. Design a Reference Architecture
- Select interface engines and API gateways that support FHIR R4, OAuth 2.0, and SMART for FHIR scopes.
- Standardize data models for demographics, orders, outcomes, and claims to make mapping easier.
4. Pilot Quick-Win Modules
- Begin with a low-risk domain, such as telehealth visit capture for behavioral health or a lab result viewer for outpatient care.
- Monitor KPIs such as clinician clicks saved, claim first-pass yield, and patient no-show rates.
5. Scale and Govern
- Create version-controlled API catalogs and run automated regression testing.
- Create a governance board with representatives from IT security, compliance, and clinical operations to assess new modules every quarter.
A staged, metrics-driven deployment enhances CEO trust while securing funding for succeeding rounds.
Vendor Selection Checklist
1. FHIR R4 and HL7 v2 Support
Modern care coordination relies on fluid data sharing; therefore, every add-on must be fluent in both FHIR and classic HL7. Request that the vendor demonstrate real-world interoperability by performing a live pull of vitals using FHIR “Observation” resources.
2. Scalability & Guaranteed Uptime
Seasonal peaks and telehealth spikes can increase transaction volumes by up to 10 times compared to the average. Confirm that the platform’s architecture auto-scales and that the contract guarantees at least 99.9% availability supported by service-credit SLAs. Request verifiable evidence—monthly uptime statistics, not marketing presentations.
3. Security and HIPAA Readiness
Every additional module increases your threat surface. Check SOC 2 Type II attestation, end-to-end encryption, and thorough Business Associate Agreements that include all subprocessors. Have the vendor go over a recent penetration test report to assess their security maturity.
4. Pricing Options are Modular and Transparent
A modular method aims to avoid all-or-nothing lock-ins. Ensure that you may license only the components you require today and add more later without incurring additional expenses. Request line-item pricing so you can predict the total cost of ownership over five years.
5. Clinician-Centered UX
Even the finest APIs will fail if the front end is frustrating for users. Check click pathways, mobile responsiveness, and customization choices. A realistic litmus test. How many clicks are required from encounter start to note sign-off? Shorter pathways are associated with increased adoption and less burnout.
Common Pitfalls (and How to Avoid Them)
| PitFall | Prevention Topic |
| API Sprawl – dozens of custom endpoints | Adopt an API gateway with versioning and throttling policies |
| Shadow IT Procurements | Enforce a governance board and security review checklist |
| Data-Model Mismatch | Mandate canonical FHIR resources, with transformation rules in middleware |
| Vendor Lock-In | Prefer open-standards connectors and data-export clauses in contracts |
| Over-Customization | Configure modules via metadata wherever possible; avoid hard-coding |
Related: Replacing Legacy EHRs with OpenEMR: A Step-by-Step Transition Blueprint
Accelerate Your Modular EHR Journey with CapMinds
Modernizing a monolithic EMR doesn’t have to drain budgets or disrupt care. CapMinds transforms legacy platforms into agile, interoperable ecosystems – exactly what your clinicians and patients need today.
Why partner with CapMinds?
- Modular EHR Architecture – We design, build, and deploy cloud-ready microservices that bolt seamlessly onto your core EMR.
- Core EMR Optimization – Fine-tune existing workflows, data models, and interfaces to maximize uptime and clinical efficiency.
- FHIR & HL7 Integration – Implement enterprise-grade API gateways and interface engines for real-time lab, telehealth, and device data exchange.
- Telehealth-Ready UX – Embed video visits, automated coding, and remote patient monitoring into one intuitive clinician screen.
- Security & Compliance – End-to-end SOC 2-certified development, HIPAA-ready hosting, and continuous penetration testing keep data safe.
From strategic roadmap through go-live support, CapMinds delivers the expertise, accelerators, and governance frameworks that keep modernization projects on time and under budget.
Let’s turn your EMR into a future-proof care platform – schedule a free discovery call today.